About Oman
Brief History of Oman
On the 23rd of July, 1970, Sultan Qaboos bin Said Al Said came to power. From the beginning of his reign, His Majesty paid enough attention to balancing tribal, regional, and ethnic interests in composing the national administration. The Council of Ministers, which functions as a cabinet, consists of 26 ministers, all directly appointed by Qaboos. The Majlis Al-Shura (Consultative Council) has the mandate of reviewing legislation pertaining to economic development and social services prior to its becoming law. The Majlis Al-Shura may request ministers to appear before it.
In November 1996, Sultan Qaboos presented his people with the "Basic Statutes of the State", Oman's first written "constitution". It guarantees various rights within the framework of Qur'anic and customary law. It partially resuscitated long dormant conflict-of-interest measures by banning cabinet ministers from being officers of public shareholding firms. Perhaps most importantly, the Basic Statutes provide rules for setting Sultan Qaboos' succession.
In September 2000, about 100,000 Omani men and women elected 83 candidates, including two women, to seats in the Majlis Al-Shura. In December 2000, Sultan Qaboos appointed the 48-members Majlis Al Dowla, or State Council, including five women. The council acts as the upper chamber in Oman's bicameral representative body.
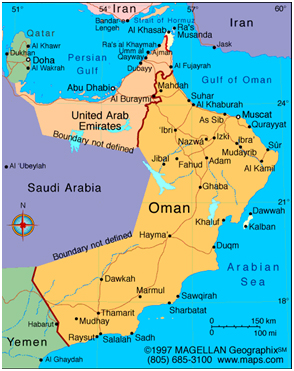
Oman occupies a strategic location on the Strait of Hormuz at the entrance to the Persian Gulf, 35 miles (56 km) directly opposite Iran. Oman has accorded great importance to regional stability and security, due to His Majesty’s wisdom, the Sultanate has maintained its diplomatic relations with the neighboring countries even and especially during critical periods of time while at the same time supporting and abiding by the laws of the United Nations.
His Majesty’s extensive modernization program has opened the country to the outside world and has preserved a long-standing political and military relationship with the United Kingdom, the United States, and others. Oman's moderate, independent foreign policy has sought to maintain good relations with all Middle Eastern countries.
Currency
The currency of Oman is the Omani Rial (OMR) divided into 1,000 baisa. Notes come in denominations of 50, 20, 10, 5 and 1 rials, and 500 and 100 baiza. Foreign currency and travellers cheques can be exchanged at banks, exchange bureaus, hotels and at the airport. Outside banking hours, money exchangers operate between 4:00 pm and 7:00 pm in the evenings and at weekends. US Dollars are recommended. American Express, MasterCard and Visa credit cards are readily accepted in large shops and hotels and by an increasing number of traders in the souks.
Cost of Living
The cost of living in Oman when compared to that in western countries is similar. Yet, your living expenses will depend on the lifestyle you choose to have. Buying goods that are recognized brand names cost more than the local brands which are usually of comparable good quality and are sometimes even better.
Culture
The Omani culture has its roots firmly grounded in the Islamic religion. Oman developed its own particular form of Islam called Ibadhism, after its founder, Abdullah ibn Ibadh who lived during the 7th Muslims. Omanis are not only tolerant of the beliefs of different Muslim divisions, they are also tolerant
towards believers of other faiths, who are allowed to practice their religion in churches and temples. Islam is based on the fulfillment of the Five Pillars of Islam, or the hadiths. By fulfilling these duties, one is assured of a place in heaven.
All Muslims are obliged to fast during the holy month of Ramadhan, one of the Pillars of Islam. For around 29- 30 days, each Islamic year, Muslims refrain from smoking, eating and drinking during the hours of fasting (from sunrise to sunset). Ramadhan advances 10 to 11 days each year as it is governed by the lunar calendar.
The Haj or pilgrimage is another Pillar of Islam. The pilgrims travel to al-Medina in Saudi Arabia to visit the Prophet’s tomb before travelling to the holy sites in Mecca. In 1999, there were approximately 19,000 Muslims travelling from Oman to Saudi Arabia. The pilgrimage is organized and coordinated by the Ministry of Religious Affairs, which ensures the pilgrims’ health and safety during the course of their stay.
National Day
Oman’s National Day is celebrated every year on the 18th November. It is a huge celebration in Oman which goes live for the whole month. The official venue of celebrations changes each year and events usually include camel racing, dancing and fireworks.
For more details about Sultanate of Oman, please visit this website of Ministry of Information (http://www.omanet.om/english/home.asp )